updated 2016-03-03
How to take-upload your visitors webcam photo
How to upload a jpg photo on your website
with your visitors webcam
html5 webcam getUserMedia examples and demo
How to take a jpg webcam photo with html5
One of the really cool things that has come from HTML5 is the ability to access a website visitor’s webcam and upload a snapshot through the browser – with the visitors permission.
example

Remove Adobe Flash!
“If you have Adobe Flash on your computer, and most of you do, you are probably being spied on and Adobe does their best not to let you know or do anything about it. Fundamentally, rich video content is the drug Adobe wants you to get hooked on, but make no mistake, one of the main purposes of Flash is apparently to secretly compromise your security. … Flash has been riddled with exploitable vulnerabilities.” [since 2009]See our page Flash takes over your camera and microphone and writes permanent cookies!
The getUserMedia API
One bad thing about it is that each browser had to rename the API instead of supporting the API as defined – so we are stuck with having an ugly multiple “if” hunting to find the right one.
example 1.
<script>
navigator.getUserMedia = (navigator.getUserMedia ||
navigator.webkitGetUserMedia ||
navigator.mozGetUserMedia );
if (navigator.getUserMedia)
{
navigator.getUserMedia(
{
video:true,
audio:false
},
function(stream) { /* do-say something */ },
function(error) { alert('Something went wrong. (error code ' + error.code + ')');
return; }
);
}
else {
alert("Sorry, the browser you are using doesn't support the HTML5 webcam API");
return;
}
</script>
from http://html5hub.com/using-the-getusermedia-api-with-the-html5-video-and-canvas-elements/
“Audio/Video capture has been the “Holy Grail” of web development for a long time. For many years we’ve had to rely on browser plugins (Flash or Silverlight) to get the job done.”
“HTML5 to the rescue. It might not be apparent, but the rise of HTML5 has brought a surge of access to device hardware. Geolocation (GPS), the Orientation API (accelerometer), WebGL (GPU), and the Web Audio API (audio hardware) are perfect examples. These features are ridiculously powerful, exposing high level JavaScript APIs that sit on top of the system’s underlying hardware capabilities.”
“getUserMedia() has been supported since Chrome 21, Opera 18, and Firefox 17.” [also Opera Mobile for Android devices]
http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/getusermedia/intro/
So far, IE and Safari don’t support getUserMedia. – almost all other browsers do.
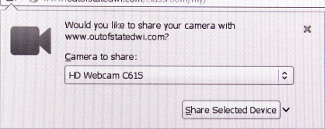
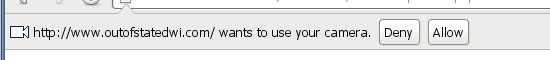
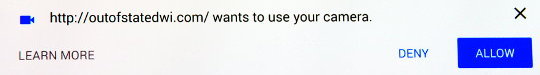
When the webcam is called the user will be asked for permission (as in the 3 images above) letting you Allow (Chrome and android) access to your camera or to “Share Selected Device”(Firefox). This is a very important privacy feature which stops websites from being able to spy on users without their knowledge. [as is being done in Flash!]
example 2.
A Complete example to get a snapshot
and upload it to the server
Pieced together from a variety of google searches and then experimenting till I got it to work.
captures a picture from webcam and submits it in a form.
Part 1. a few CSS styles:
<style>
.camcontent{
display: block;
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
height: 480px;
margin: auto;
}
.cambuttons button {
border-radius: 15px;
font-size: 18px;
}
.cambuttons button:hover {
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 15px;
background: #00dd00 ; /* green */
}
</style>
Part 2. the Javascript and HTML5:
Note: A small google script is used to avoid “reinventing the wheel”.
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.8.3/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
// Put event listeners into place
window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
// Grab elements, create settings, etc.
var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas"),
context = canvas.getContext("2d"),
video = document.getElementById("video"),
videoObj = { "video": true },
image_format= "jpeg",
jpeg_quality= 85,
errBack = function(error) {
console.log("Video capture error: ", error.code);
};
// Put video listeners into place
if(navigator.getUserMedia) { // Standard
navigator.getUserMedia(videoObj, function(stream) {
video.src = stream;
video.play();
$("#snap").show();
}, errBack);
} else if(navigator.webkitGetUserMedia) { // WebKit-prefixed
navigator.webkitGetUserMedia(videoObj, function(stream){
video.src = window.webkitURL.createObjectURL(stream);
video.play();
$("#snap").show();
}, errBack);
} else if(navigator.mozGetUserMedia) { // moz-prefixed
navigator.mozGetUserMedia(videoObj, function(stream){
video.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(stream);
video.play();
$("#snap").show();
}, errBack);
}
// video.play(); these 2 lines must be repeated above 3 times
// $("#snap").show(); rather than here once, to keep "capture" hidden
// until after the webcam has been activated.
// Get-Save Snapshot - image
document.getElementById("snap").addEventListener("click", function() {
context.drawImage(video, 0, 0, 640, 480);
// the fade only works on firefox?
$("#video").fadeOut("slow");
$("#canvas").fadeIn("slow");
$("#snap").hide();
$("#reset").show();
$("#upload").show();
});
// reset - clear - to Capture New Photo
document.getElementById("reset").addEventListener("click", function() {
$("#video").fadeIn("slow");
$("#canvas").fadeOut("slow");
$("#snap").show();
$("#reset").hide();
$("#upload").hide();
});
// Upload image to sever
document.getElementById("upload").addEventListener("click", function(){
var dataUrl = canvas.toDataURL("image/jpeg", 0.85);
$("#uploading").show();
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "html5-webcam-save.php",
data: {
imgBase64: dataUrl,
user: "Joe", *
userid: 25 *
}
}).done(function(msg) {
console.log("saved");
$("#uploading").hide();
$("#uploaded").show();
});
});
}, false);
</script>
<div class="camcontent">
<video id="video" autoplay></video>
<canvas id="canvas" width="640" height="480">
</div>
<div class="cambuttons">
<button id="snap" style="display:none;"> Capture </button>
<button id="reset" style="display:none;"> Reset </button>
<button id="upload" style="display:none;"> Upload </button>
<br> <span id=uploading style="display:none;"> Uploading has begun . . . </span>
<span id=uploaded style="display:none;"> Success, your photo has been uploaded!
<a href="javascript:history.go(-1)"> Return </a> </span>
</div>
Above, there are 2 or 3 lines which you may need to change to fit your situation:
(of course, you can change a lot – especially the css and html)
1. the name of the program ajax calls and sends the image and other data to is named “html5-webcam-save.php” in this example and the example code for it is in “Part 3.” below. Realize that the name of your program is arbitrary and if you write programs using another language (not php), that is your option also.
2. in addition, you can send other information along with the image.
“imgBase64: dataUrl”
is required but the examples *
user: “Joe”,
userid: 25
are not likely useful. You will want to put in variables that identify the person. like for instance:
userid: "<?php echo $USER->id ; ?>"
This php example is one where the visitor/user has logged in to some website program and their user-id is being stored in memory, in a variable “$USER->id”. If it is a number, the quotes are ok but not required, if it contains characters other than numbers, the quotes are required.
Part 3. the “html5-webcam-save.php”
to save the .jpg photo to a folder (ex: images/) using php:
Break up a string on the commas (“explode”), convert (decode) the jpg image, name and save the image.
(and maybe update a user record in your database?)
<?php
$rawData = $_POST['imgBase64'];
$filteredData = explode(',', $rawData);
$unencoded = base64_decode($filteredData[1]);
$datime = date("Y-m-d-H.i.s", time() ) ; # - 3600*7
$userid = $_POST['userid'] ;
// name & save the image file
$fp = fopen('images/'.$datime.'-'.$userid.'.jpg', 'w');
fwrite($fp, $unencoded);
fclose($fp);
// next, update or insert a users record
part 4. extra: How to retrieve and view the collection
of photos saved in the folder “images” with php
<?php
$filelist = opendir('images') ;
$photos = array();
while ($campic = readdir($filelist))
{
if (strpos($campic, '.jpg') !== false )
{ $photos[] = $campic; }
}
closedir($filelist);
rsort($photos); # to display the most recent photos first
foreach ($photos AS $photo )
{ echo ' <img width=640 height=480 src="images/'.$photo.'">
<br> '.$photo.'<br> <br> <br>' ; }
Awesome work done…
lots of thanks dude…….. 🙂
you are welcome!
Hi great article but i have a question for you hoping you can help/email me. i have a document scanner which has a 5 meg resolution camera. it is basically a webcam. i want to take photographs of documents at 5 meg but only show the stream at a lower resolution say 800 x 600 and in a smaller canvas. when i press click i want to save the 5 meg stream as png or jpeg or pdf. i might need to rotate the picture because it scans horizontal and the document should be displayed vertically. can you help me because i am at a loss. thanks joe
Your scanner should have an option for different resolutions, formats (jpg etc.), rotation, etc. Even if it does and the options you want are not offered, you will need to use a photo editor to resize the images, or change format, etc., after that to get what you want.
This is an awesome article. Is there a way to add a form box to have the user input the user id and pass it along to the PHP? I’ve got a working form to specify the variable in the URL, but I can’t seem to get the PHP to catch it.
take a look at the variables in memory. It should already be there.
example:
echo '<pre>'; var_dump ( get_defined_vars() ); echo '</pre>';Great great great! Best article about webcam + html5!
I just got problems with the preview image. I want it smaller, but it’s always 640×480. Even trying to modify css and JS, it keeps in this resolution. So when I use it in my cellphone it’s getting to big.
Congrats! Great work!
I’ve got it! Just edited the style of video tag. 🙂 Perfect.
glad you got it.
Thanks! This is awesome!
You are welcome!
Good Day, I have a project that involves a pentab for signatures is it possible to apply it here using your code?
tell me please, after save image into folder and then save to mysql database
it is possible that, in step 3, you will also want to write or update a record in your database.
help me please, adding insert into database
insert into image (name_image) values ($fb);
Thanks a lot for the help so far. I’m having trouble implementing the php part though. Do I simply copy-paste it into a notepad and save it in the web root folder?
definitely use an editor like notepad, NOT a word processor. you can put it at the root of your site till you get it running and then put it in a folder and spell out the path.